While traditional smoothing methods use the same window shape and size to smooth an image independent of the local image content, in adaptive smoothing, the window shape and size are adapted to the local image content. In adaptive smoothing, a window is sized according to the local gradient magnitude and shaped in such a way that it has a shorter side across an edge than along the edge. This mechanism maintains edge details while smoothing random noise. Adaptive smoothing reduces noise similar to traditional smoothing but unlike traditional smoothing it does not blur the edges (as much). Examples of adaptive image smoothing are given below. |

Fig. 1. (Left) An image corrupted by impulse noise. (Center) Traditional median filtering. (Right) Adaptive median filtering. The two
results look alike at first glance, but when examined more closely, it is clear that small details are preserved by the adaptive
method better than by the traditional method.
results look alike at first glance, but when examined more closely, it is clear that small details are preserved by the adaptive
method better than by the traditional method.



Fig. 2. (Left) An image corrupted by impulse noise. (Middle) Traditional median filtering. (Right) Adaptive median filtering. Small
details are preserved by the adaptive method but smoothed by the traditional method.
details are preserved by the adaptive method but smoothed by the traditional method.



Fig. 3. (Top left) Image corrupted with white noise. (Top middle) Image smoothed usingy traditional mean filtering. (Top right)
Image smoothed using adaptive mean filtering. (Bottom left) Image smoothed using traditional Gaussian filtering. (Bottom right)
Image smoothed using adaptive Gaussian filtering. The difference between adaptive and traditional methods should be obvious.
Image smoothed using adaptive mean filtering. (Bottom left) Image smoothed using traditional Gaussian filtering. (Bottom right)
Image smoothed using adaptive Gaussian filtering. The difference between adaptive and traditional methods should be obvious.




Fig. 4. (Top left) Image corrupted with white noise. (Top middle) Image smoothed using traditional mean filtering. (Top right) Image
smoothed using adaptive mean filtering. (Bottom left) Image smoothed using traditional Gaussian filtering. (Bottom right) Image
smoothed using adaptive Gaussian filtering.
smoothed using adaptive mean filtering. (Bottom left) Image smoothed using traditional Gaussian filtering. (Bottom right) Image
smoothed using adaptive Gaussian filtering.
To obtain a software license for this adaptive smoothing, follow this link =>


| Adaptive smoothing |
| Image Registration and Fusion Systems |



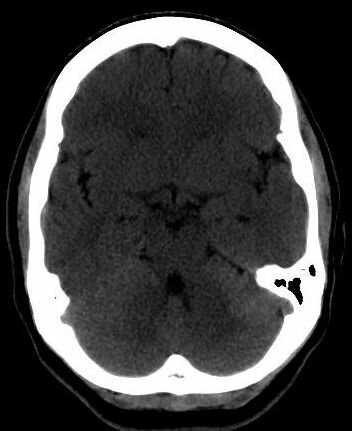
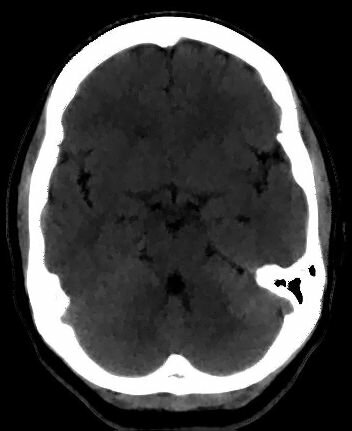
(a) (b)
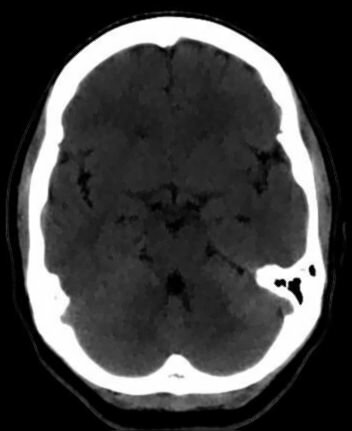
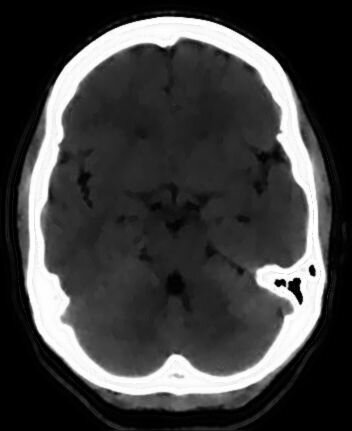
(a) (b)
Fig. 5. (a) A CT brain slice. This image is courtesy of MedPix. Smoothing of the CT image with (b) an adaptive median filter, (c) an
adaptive mean filter, and (c) an adaptive Gaussian filter.
Fig. 5. (a) A CT brain slice. This image is courtesy of MedPix. Smoothing of the CT image with (b) an adaptive median filter, (c) an
adaptive mean filter, and (c) an adaptive Gaussian filter.
